
This chemical element is used in chemical industry for producing insecticides, pesticides, sedatives, and other chemicals. In nature, it can be found in some deposits in the soils, which are in abundance in North America and China, as well as in the Dead Sea. Bromine belongs to the group of halogens. This chemical element exists in our cells in the form of bromide, but in large doses it has very strong irritating and toxic properties so it should be avoided. That is why its name comes from a Greek word meaning stench.

doi: 10.Bromine is a toxic oily liquid of intense red color, known for its strong unpleasant smell. Boca Raton, Florida: Chemical Rubber Company Publishing. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (92nd ed.). “ Ab initio studies of solid bromine under high pressure”. Xylyl bromide and related bromine compounds were used as poison gas in World War I.The Dow Chemical Company got its start when Herbert Dow separated bromine from brine waters of the Midwestern United States.Bromothymol blue is a bromine-based pH indicator.The ancient royal purple dye called Tyrian Purple is a bromine compound.Its use is banned in Europe, but not in the United States. Long-term exposure causes neurological symptoms. Brominated vegetable oil is a food additive that keeps citrus flavoring from separating out of soda.Although this is the most common state for bromine and other halogens, it isn’t the only one. Bromides are compounds that contain bromine in its -1 oxidation state.Magnetic Ordering: Diamagnetic Interesting Bromine Facts Heat of Vaporization: (Br 2) 29.96 kJ/mol

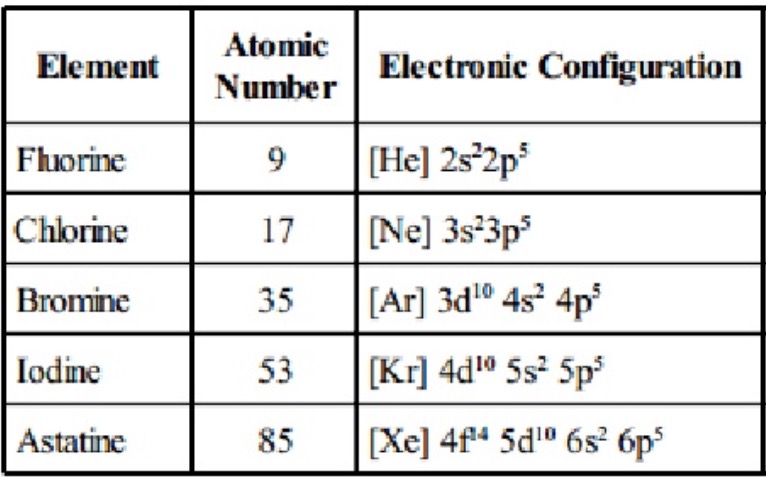
Bromine was used in leaded fuels to help prevent engine knock in the form of ethylene bromide. However, they are not generally useful because they are expensive and because they damage the ozone layer. Nontoxic halomethane compounds, such as bromochloromethane and bromotrifluoromethane, are used in submarines and spacecraft. Bromine is used to make brominated plastics and polymers. Bromine is used to sanitize swimming pools, much like chlorine. The acid acts as a flame retardant by interfering with the oxidation reaction of combustion. When brominated compounds burn, hydrobromic acid is produced. Uses: Bromine is used in many flame retardant compounds. Specifically, sodium bromide and potassium bromide were used in the 19th and 20th century until they were replaced by chloral hydrate, which was in turn replaced by barbiturates and other drugs. Bromide compounds used to be used as sedatives and anticonvulsants. Bromine also helps white blood cells kill parasites and serves a role in REM sleep. The bromide ion is a cofactor in collagen synthesis. However, bromine is an essential element in animals. Inhalation can cause irritation, in low concentrations, or death, in high concentration. Commercially, bromine is extracted from bromine pools in Israel, the United States, and China.īiological Role: Like chlorine, elemental bromine is a toxic substance that causes chemical burns to skin. It is the is the tenth most abundant element in sea water with an abundance of 67.3 mg/L. The most stable isotope is 77Br, with a half-life of 57.04 hours.Ībundance: Bromine is the 64th most abundant element in the Earth’s crust with an abundance of 2.4 mg/kg. Numerous radioisotopes have been synthesized. Isotopes: Natural bromine consists of two stable isotopes: 79Br and 81Br, with 79Br accounting for 51% of the natural abundance of the element. Eventually, the element name changed to bromine to use the -ine halogen name suffix. But, he changed the name to brôme in his publication, from the Greek word for “stench.” The name comes from the acrid smell of bromine vapor. Name Origin: Balard named the new element muride, from the Latin word for brine, muria. In 1825, German chemist Justus von Liebig also isolated a brown liquid from a sample of salt water, but he didn’t realize it was a new element until after he learned of Balard’s publication. Balard isolated bromine from seaweed ash taken from a salt marsh of Montpellier, France. Löwig isolated the element from a mineral water spring taken from his home town of Bad Kreuznach, Germany. Although Löwig discovered the element first, Balard published his results first. (photo: Alchemist-hp)Ītomic Mass: conventional: 79.904Įlectron Configuration: 3d 10 4s 2 4p 5ĭiscovery: Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Balard discovered the element bromine in 18, respectively. Bromine is a reddish-brown liquid at room temperature and pressure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
